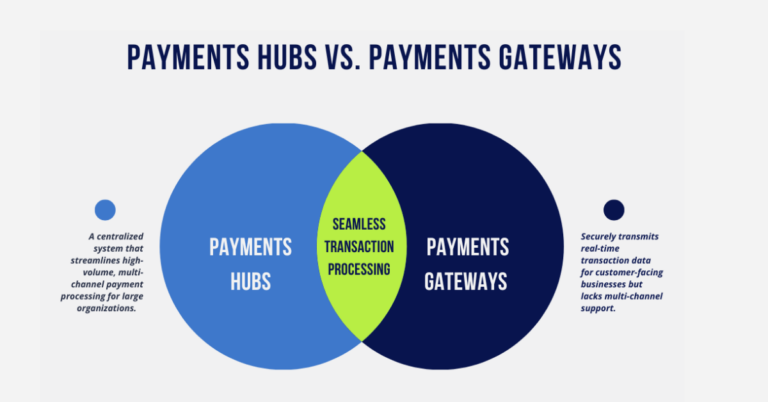
Electronic bill presentment and payments (EBPP) can sometimes feel like a swirl of acronyms and industry jargon. The first step toward a deeper comprehension of EBPP is a better understanding of the terminology associated with it. We created this shortlist of 11 commonly used terms to help get you started.
EBPP
An acronym for electronic bill presentment and payments, EBPP refers to the technology that allows organizations to present bills to their customers and accept payments for those bills. For example, Orbipay EBPP is a solution used by companies across a variety of industries (auto finance, banking, healthcare, and insurance, for example) that notifies customers when their bills are due, presents the details of those bills, and accepts payments to settle the associated balances.
Merchant
A merchant is an individual, business, or entity that sells goods and/or services for a profit. In EBPP, the term merchant is interchangeable with biller.
Payment Channels
A comprehensive term for the various outlets that customers can use to make bill payments. Payment channels may include mail, walk-in, agent, web/mobile, interactive voice response (IVR), messaging apps like Facebook Messenger, and intelligent personal assistants like Amazon Alexa and Google Assistant.
Payment Options
Refers to the options that dictate the frequency of bill payments made on the underlying account. Payment options can be broken down into two sub-categories:
- Single Payments including One Time, Balance Reload, and Skip-A-Payment
- Repeating Payments including Recurring, AutoPay, and Payment Plans
Payment Methods
An umbrella term for the types of payments that customers can use to pay their bills. This may include cash, personal checks, ACH, credit cards, debit cards, and prepaid cards.
ACH
The Automated Clearing House (ACH) is an electronic network managed by NACHA that facilitates financial transactions including both credits (direct deposit and payroll, for example) and debits (bill payments, for example). The ACH network was created to support the electronic exchange of these transactions between participating institutions in the United States. A typical application of ACH for bill payments is the customer providing the routing and account number of their bank account to the biller, and the biller then pulling the funds from the customer’s account to settle the balance.
Card Networks
The card networks are comprised of American Express, Discover, Mastercard, and Visa. These companies maintain the networks that process payments between payment card issuers (often banks and credit unions) and merchant banks by charging a fee for each transaction. It’s important to note that Mastercard and Visa don’t issue their own payment cards, but American Express and Discover do.
Interchange
Card transactions have an associated interchange fee that is calculated using various factors including the type of card, the merchant accepting it, and how the payment is processed (ecommerce, EMV chip, magnetic stripe, etc.). The interchange fee is paid by the merchant to the company that issued the credit card and is usually calculated as a percentage of the sale plus a flat fee.
Convenience Fees
A convenience fee can be charged by a biller for using an alternative payment channel, or one that is not standard for the biller. The convenience fee must be a flat fee and disclosed to the customer in advance. For example, a local government’s standard payments may only include counter payments and mailed payments. If so, they might be able to assess a convenience fee for accepting online payments.
PCI DSS
PCI DSS is an acronym for the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard. The term refers to a set of data security standards applicable to all organizations that store, process, or transmit cardholder data. This standard was created to protect cardholders and the personal data they transmit when making payments. If merchants are not compliant with PCI DSS, they can face stiff fines and penalties from the card networks that are responsible for enforcing PCI DSS.
Chatbots
Chatbots, also referred to as bots, are technology powered by artificial intelligence that simulate human conversation. Common chatbots include Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple’s Siri. In EBPP, chatbots can be deployed via messaging apps and intelligent personal assistants to answer account inquiries, resolve issues, and pay bills.